EUlerian LAGrangian (EULAG)
EULAG - a numerical solver for all-scale geophysical flows
The high-performance computational model EULAG is a virtual laboratory for
advancing basic research and education in geophysical fluid dynamics.
advancing basic research and education in geophysical fluid dynamics.
It accommodates a broad class of flows and underlying fluid equations,
in a variety of domains on scales from laboratory and wind tunnel to
global. The range of physical applications addressed with EULAG is
correspondingly broad, including at one end microscopic phenomena such
as flows in porous media and planetary climate at the other.
in a variety of domains on scales from laboratory and wind tunnel to
global. The range of physical applications addressed with EULAG is
correspondingly broad, including at one end microscopic phenomena such
as flows in porous media and planetary climate at the other.
EULAG owes its versatility to a unique design that fuses a rigorous
theoretical formulation in generalized curvilinear coordinates with
nonoscillatory forward-in-time (NFT) differencing for fluids built on the
multidimensional positive definite advection transport algorithm (MPDATA)
and a robust, exact-projection type elliptic solver.
theoretical formulation in generalized curvilinear coordinates with
nonoscillatory forward-in-time (NFT) differencing for fluids built on the
multidimensional positive definite advection transport algorithm (MPDATA)
and a robust, exact-projection type elliptic solver.
Although EULAG has a proven record as a general purpose flow solver, historically, the
primary aim underlying its design was to simulate multiscale atmospheric
circulations with anelastic equations. Because of this meteorological
heritage (i.e., specialization in simulation of low Mach number, high
Reynolds number, rotating stratified flows with continuous spectra
of dispersive waves) EULAG contains features non-standard in other
areas of computational fluid dynamics, which have proven beneficial
outside meteorology including a number of contributions in stellar
magnetohydrodynamics (MHD).
The EULAG code is written as a research tool with numerous options
controlling the numerical accuracy and allowing for a wide range of
numerical sensitivity tests. These capabilities give the researcher
confidence in the numerical solutions of their problem. The formulation
of the model equations allow for various derivatives of the code
including codes for stellar atmospheres, ocean currents, sand dune
propagation, biomechanical flows as well as high speed flows and acoustic
phenomena. EULAG is a fully parallelized code and is easily portable
between different platforms.
All the model developments and details of the numerical algorithms are
documented in a number of peer reviewed papers by Piotr Smolarkiewicz
and his colleagues. The EULAG modeling system has been developed and supported
by the Mesoscale and Microscale Meteorology Laboratory of NCAR.
primary aim underlying its design was to simulate multiscale atmospheric
circulations with anelastic equations. Because of this meteorological
heritage (i.e., specialization in simulation of low Mach number, high
Reynolds number, rotating stratified flows with continuous spectra
of dispersive waves) EULAG contains features non-standard in other
areas of computational fluid dynamics, which have proven beneficial
outside meteorology including a number of contributions in stellar
magnetohydrodynamics (MHD).
The EULAG code is written as a research tool with numerous options
controlling the numerical accuracy and allowing for a wide range of
numerical sensitivity tests. These capabilities give the researcher
confidence in the numerical solutions of their problem. The formulation
of the model equations allow for various derivatives of the code
including codes for stellar atmospheres, ocean currents, sand dune
propagation, biomechanical flows as well as high speed flows and acoustic
phenomena. EULAG is a fully parallelized code and is easily portable
between different platforms.
All the model developments and details of the numerical algorithms are
documented in a number of peer reviewed papers by Piotr Smolarkiewicz
and his colleagues. The EULAG modeling system has been developed and supported
by the Mesoscale and Microscale Meteorology Laboratory of NCAR.
Example: QBO analogue simulation
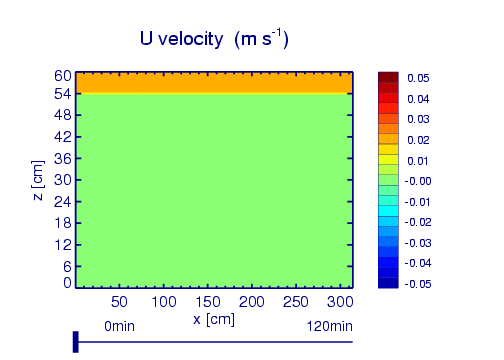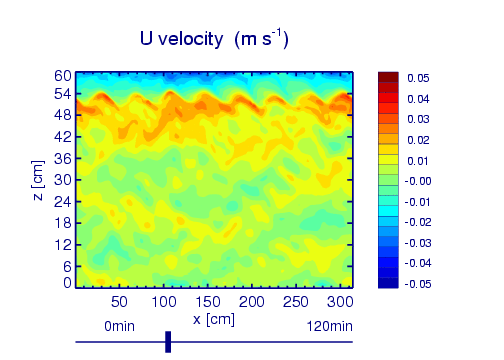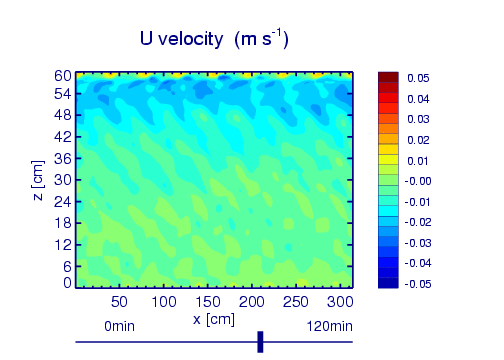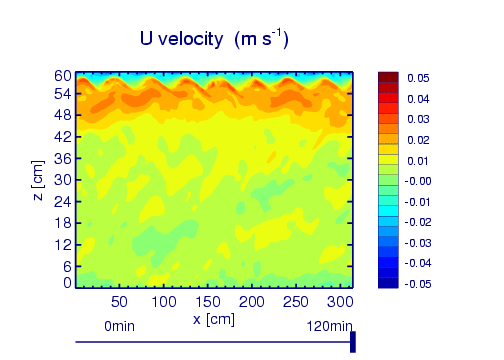
Wedi, N. P., and P. K. Smolarkiewicz (2006), Direct numerical simulation of the Plumb-McEwan laboratory analog of the QBO, J. Atmos. Sci., 63(12), 3226–3252